Push Changes
⬆️ How to Push Changes to GitHub¶
Pushing transfers commits from your local repository to a remote repository.
1. Clone & Prepare¶
Let's clone the repository:
ubuntu@manikandan:~$ git clone https://github.com/devopspilot2/firstproject.git
Cloning into 'firstproject'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 3, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done.
remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
Receiving objects: 100% (3/3), done.
ubuntu@manikandan:~$ cd firstproject/
ubuntu@manikandan:~/firstproject$ ll
total 4
-rw-rw-r-- 1 ubuntu ubuntu 14 Jun 2 23:41 README.md
In this firstproject repository we have only README.md file.
2. Make Changes¶
Let's create a new file hello.txt:
ubuntu@manikandan:~/firstproject$ echo "Created for git demo" > hello.txt
ubuntu@manikandan:~/firstproject$ ll
total 8
-rw-rw-r-- 1 ubuntu ubuntu 14 Jun 2 23:41 README.md
-rw-rw-r-- 1 ubuntu ubuntu 21 Jun 2 23:42 hello.txt
ubuntu@manikandan:~/firstproject$ cat hello.txt
Created for git demo
3. Check Status¶
Run git status to check the status of the file:
ubuntu@manikandan:~/firstproject$ git status
On branch main
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/main'.
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
hello.txt
nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
In the untracked files, its showing the newly created file hello.txt.
4. Stage & Commit¶
Run git add to track the file:
ubuntu@manikandan:~/firstproject$ git add hello.txt
ubuntu@manikandan:~/firstproject$ git status
On branch main
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/main'.
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
new file: hello.txt
Now commit the file:
ubuntu@manikandan:~/firstproject$ git commit -m "Added hello.txt for git demo"
Author identity unknown
*** Please tell me who you are.
Run
git config --global user.email "you@example.com"
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
to set your account's default identity.
Omit --global to set the identity only in this repository.
fatal: unable to auto-detect email address (got 'ubuntu@manikandan.(none)')
The command has failed, since the author name and email id is not configured. This is a one-time activity.
Configure Identity:
ubuntu@manikandan:~/firstproject$ git config --global user.email "devopspilot2@gmail.com"
ubuntu@manikandan:~/firstproject$ git config --global user.name "Vignesh Sweekaran"
Verify configuration:
ubuntu@manikandan:~/firstproject$ git config -l --global
user.email=devopspilot2@gmail.com
user.name=Vignesh Sweekaran
Retry Commit:
ubuntu@manikandan:~/firstproject$ git commit -m "Added hello.txt for git demo"
[main d26925d] Added hello.txt for git demo
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 hello.txt
5. Push to Remote¶
Run git push origin main. It will ask for username and password.
Note: You must use a Personal Access Token (PAT) as the password.
Generating a PAT: 1. Click your profile photo -> Settings.
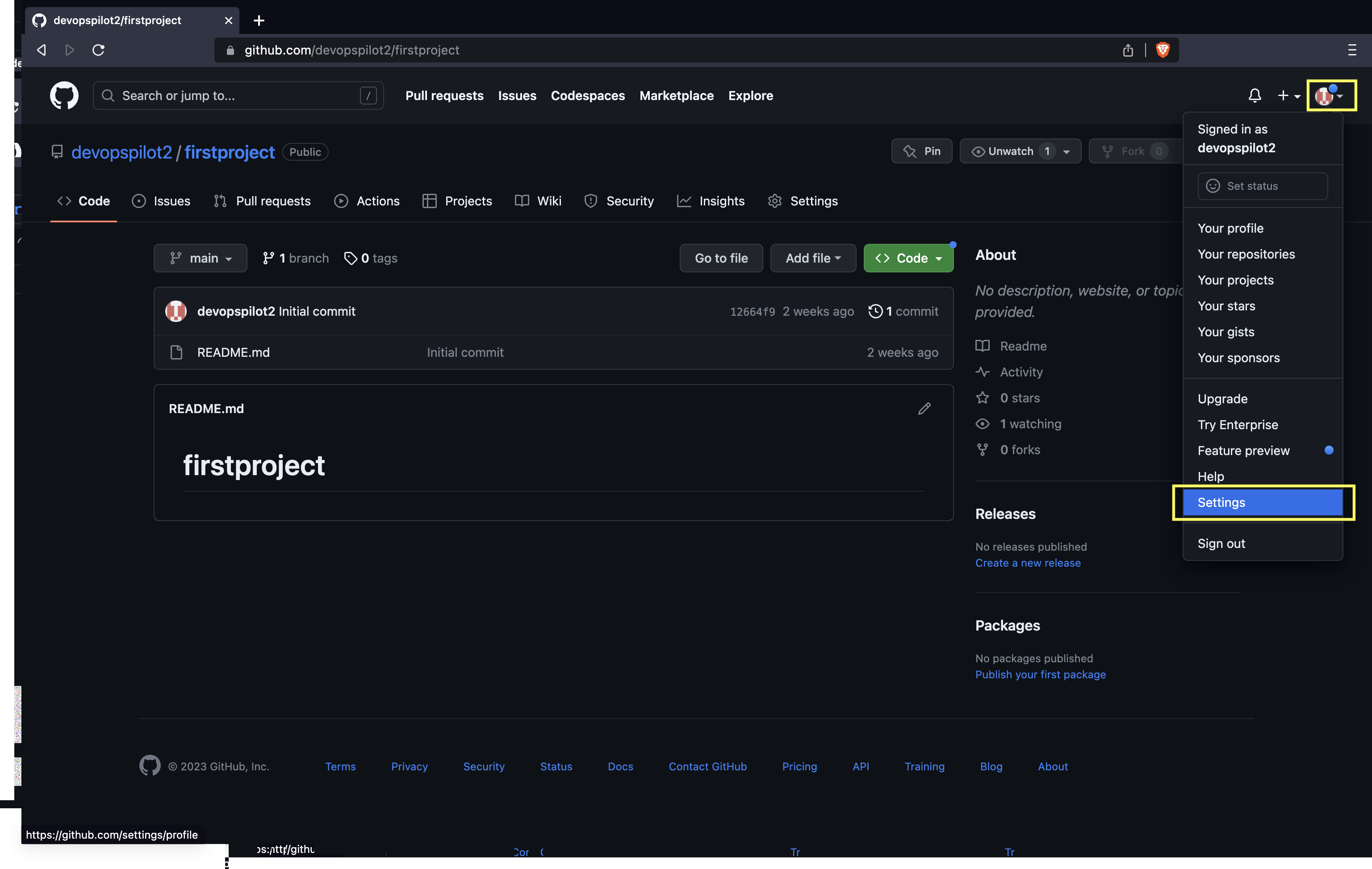
- Click on Developer settings.
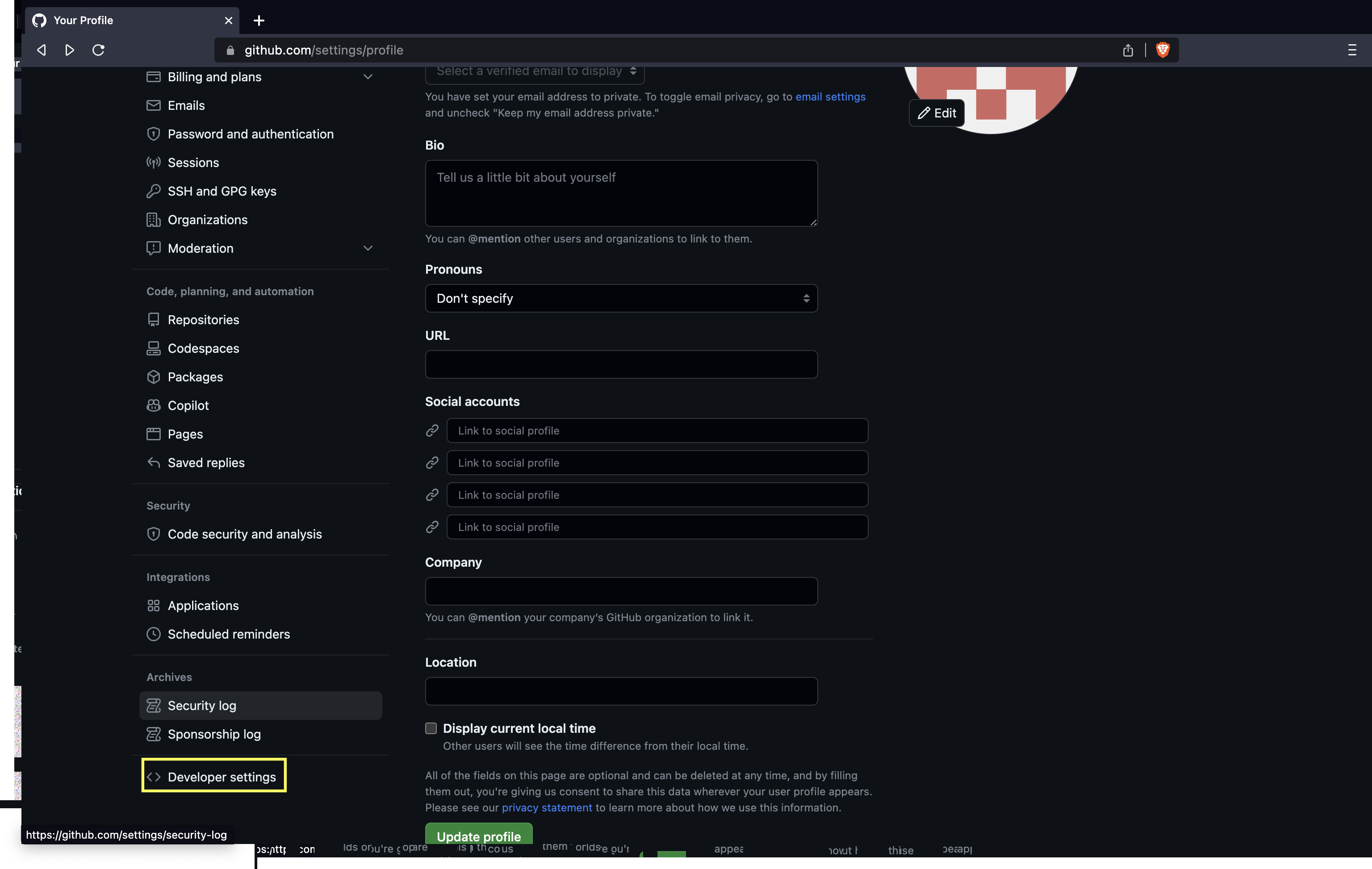
- Click on Personal access tokens and then Tokens (classic).
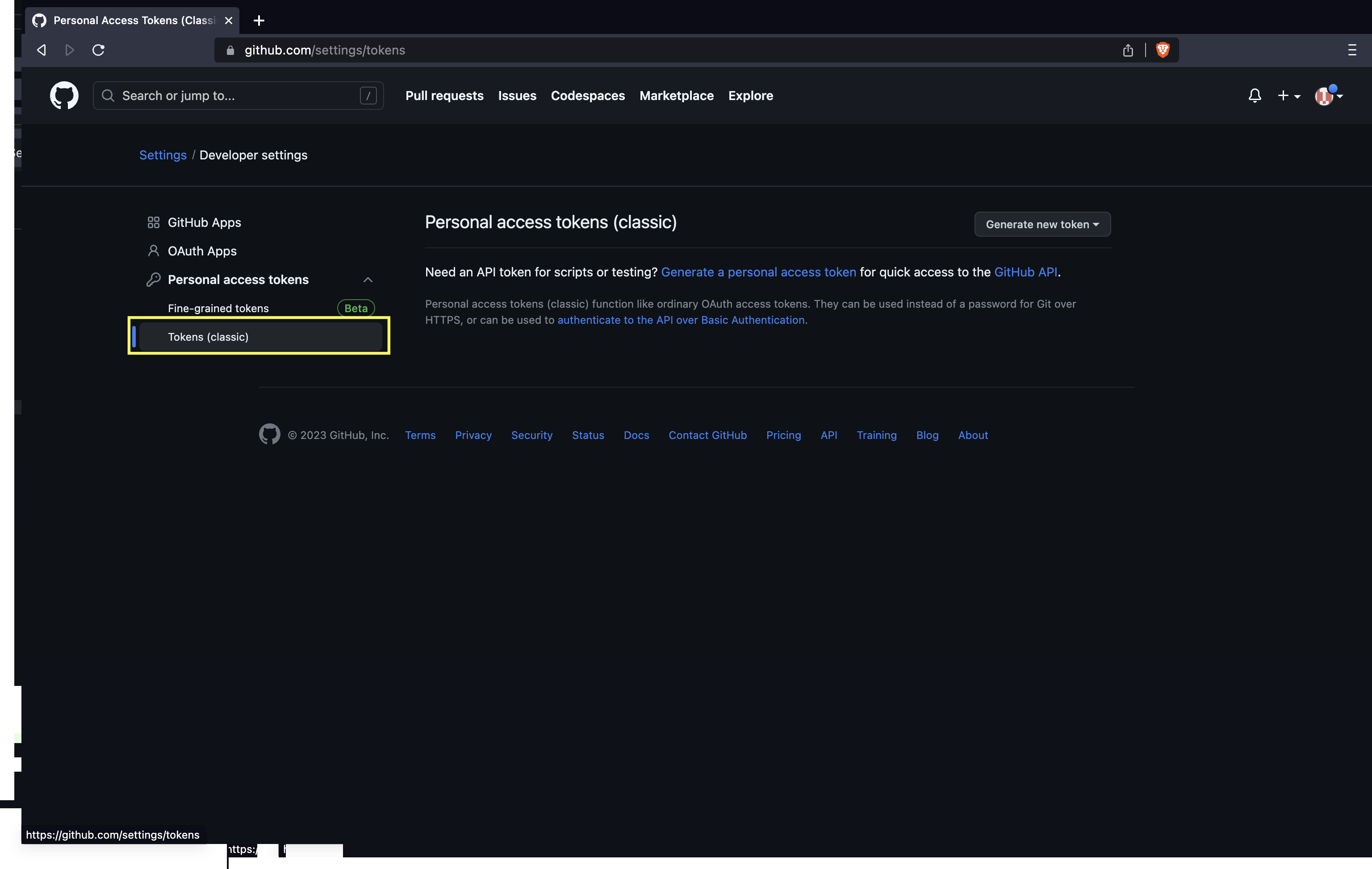
- Click on Generate token and then Generate new token (classic).
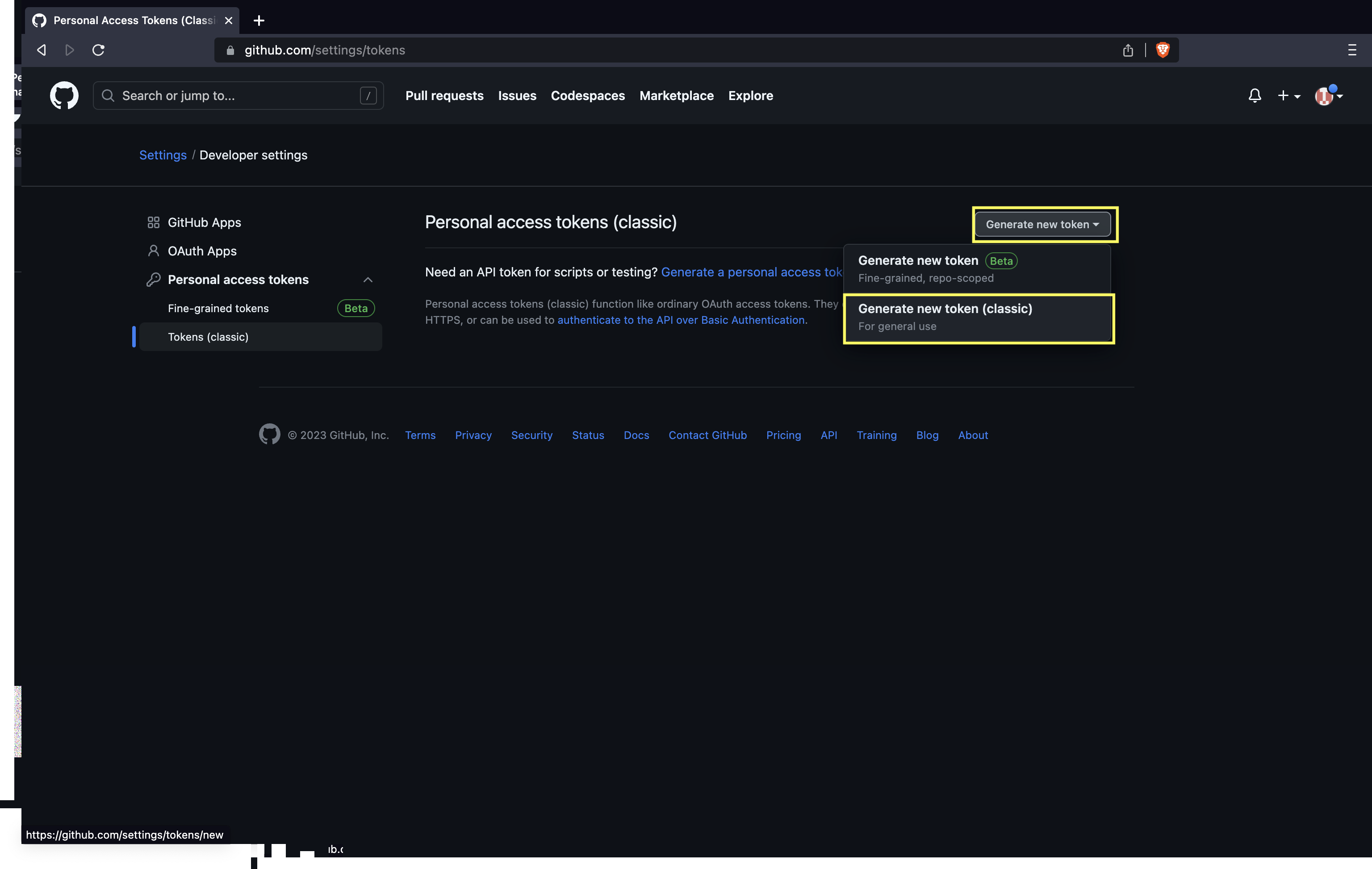
- Name the token and check the
repobox.
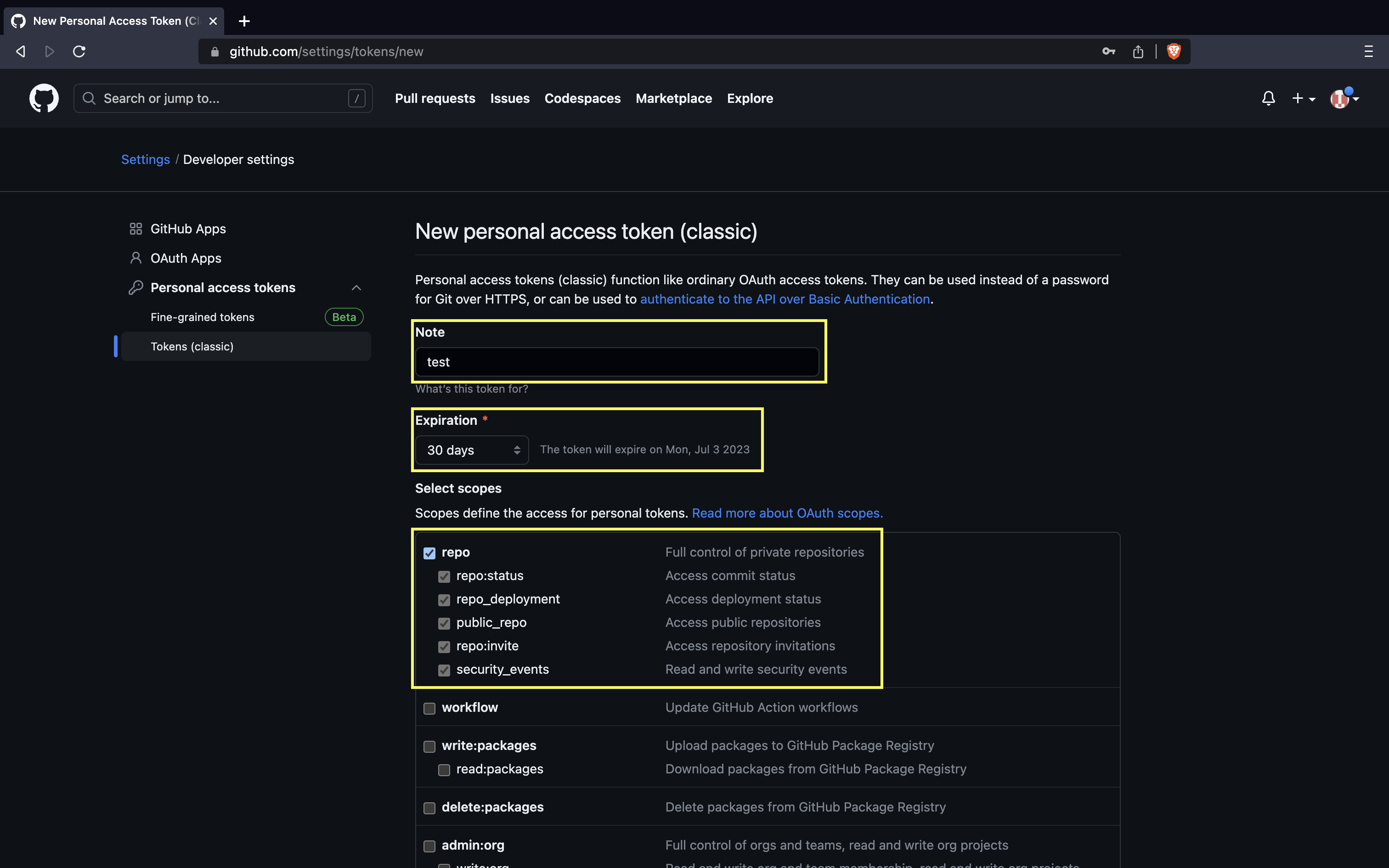
- Click Generate token.
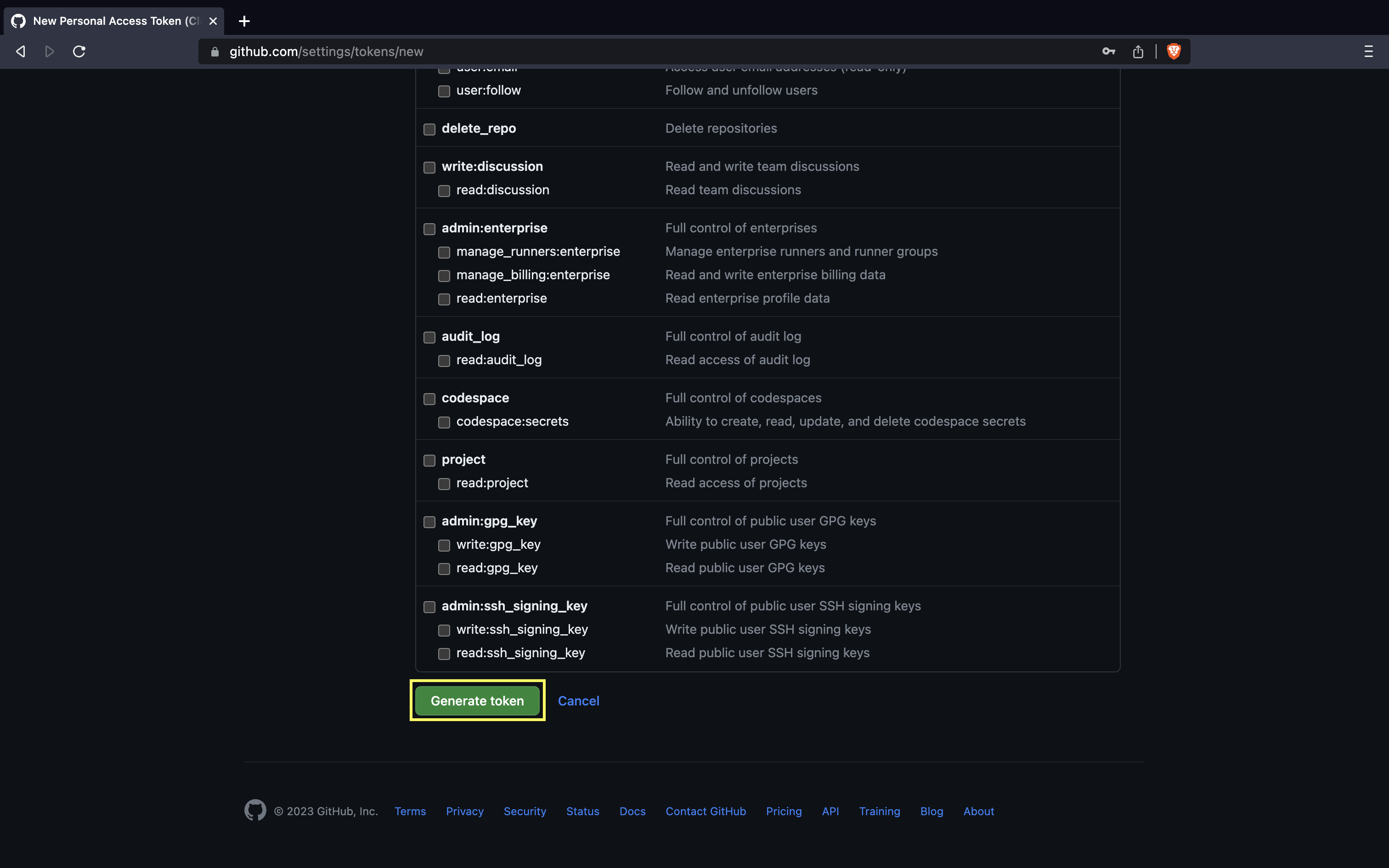
- The Personal access token(PAT) is shown only one time. Copy and save in secure place.
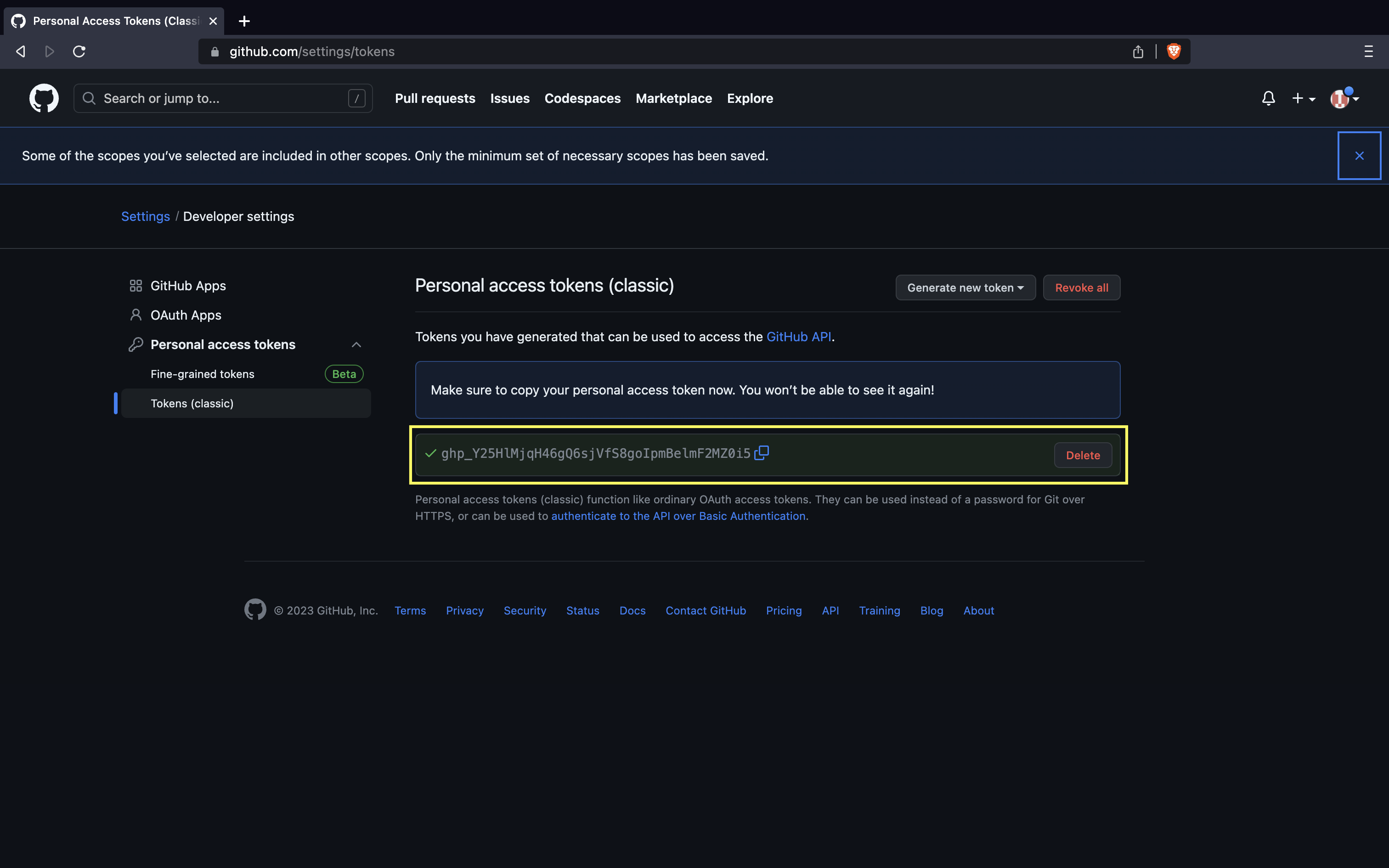
Now, use the PAT as the password:
ubuntu@manikandan:~/firstproject$ git push origin main
Username for 'https://github.com': devopspilot2
Password for 'https://devopspilot2@github.com':
Enumerating objects: 4, done.
Counting objects: 100% (4/4), done.
Delta compression using up to 2 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 322 bytes | 322.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
To https://github.com/devopspilot2/firstproject.git
12664f9..d26925d main -> main
The hello.txt is now pushed to GitHub!
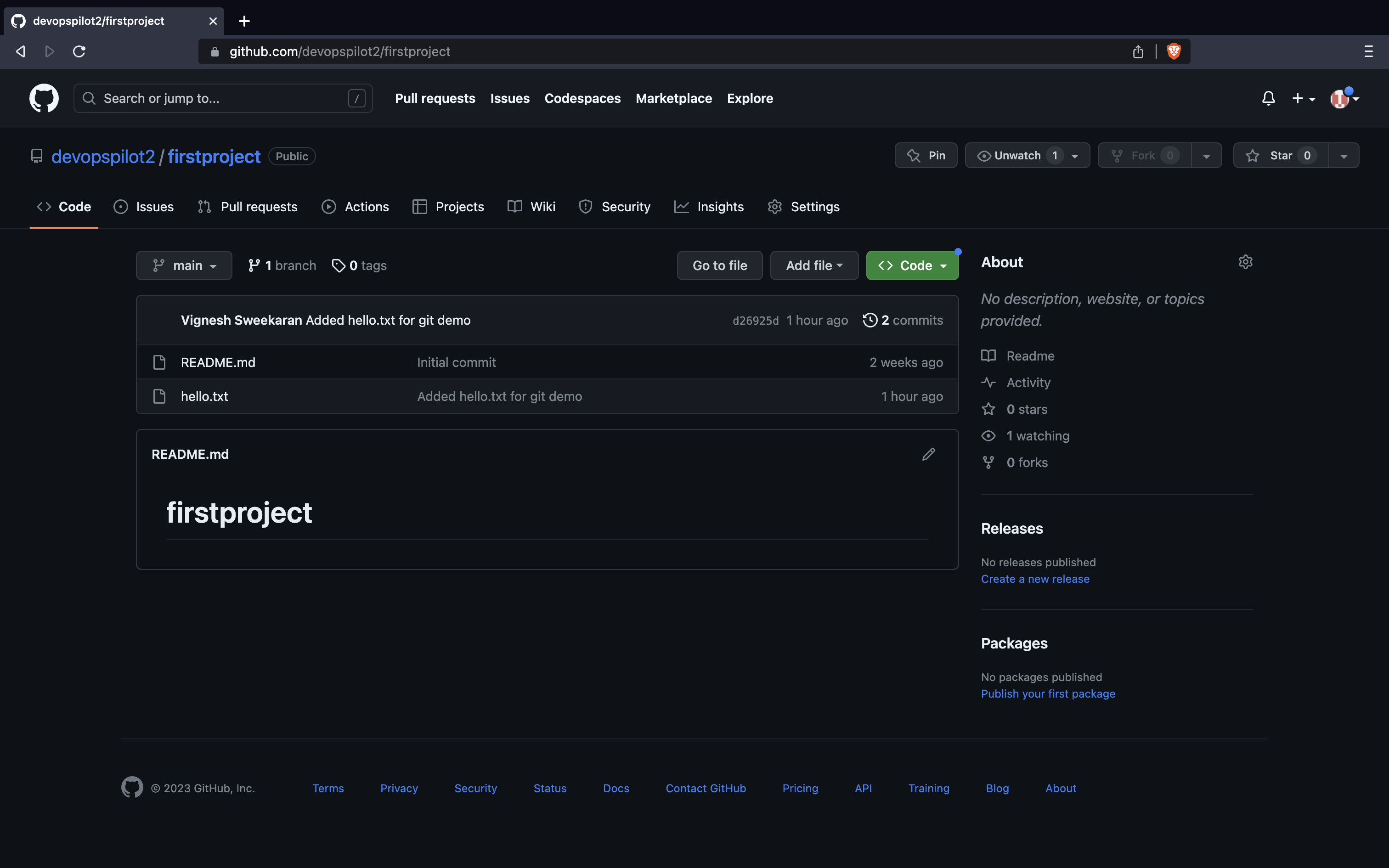
📜 Verify on GitHub¶
Go to your repository on GitHub and click Commits to see your changes.
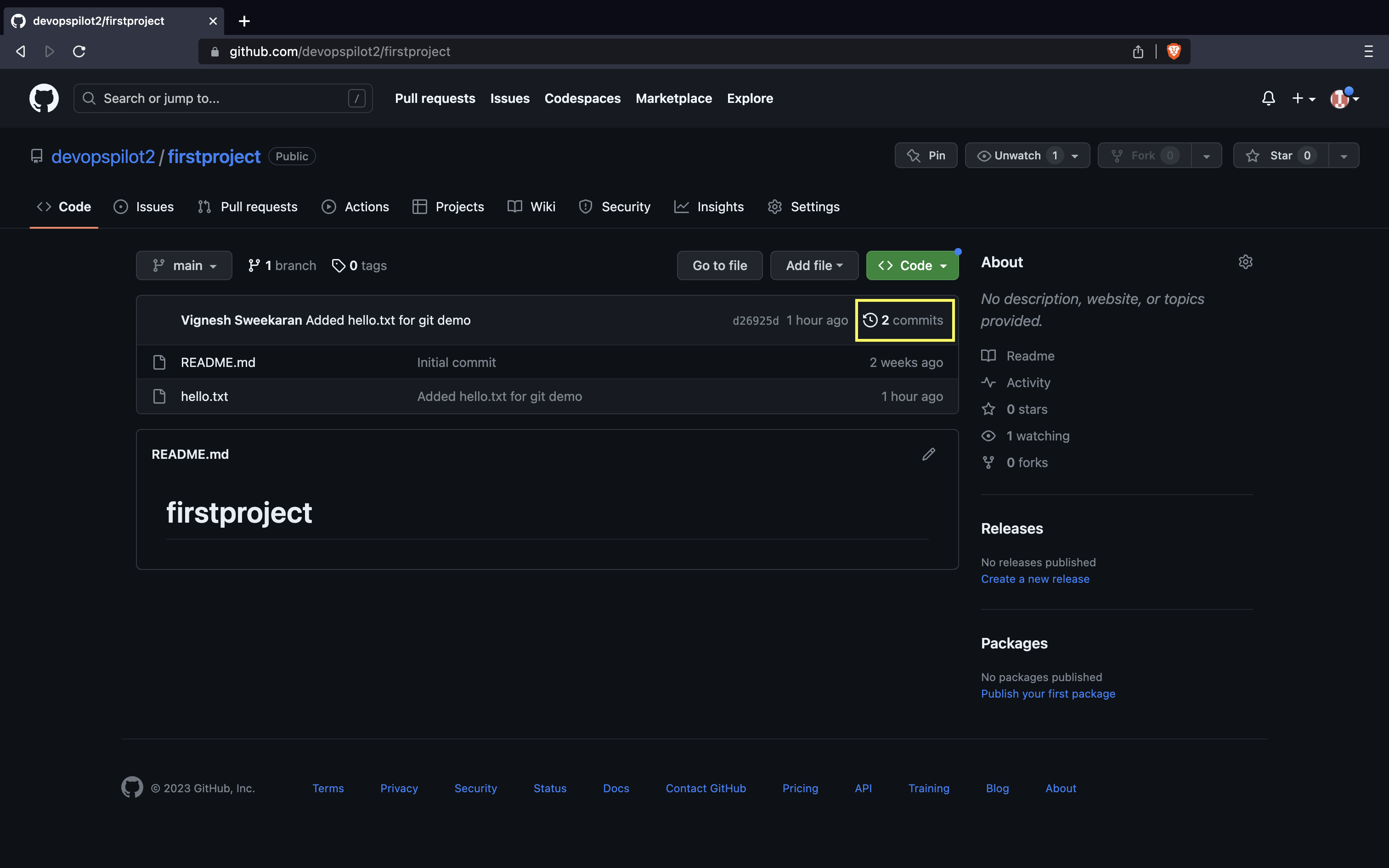
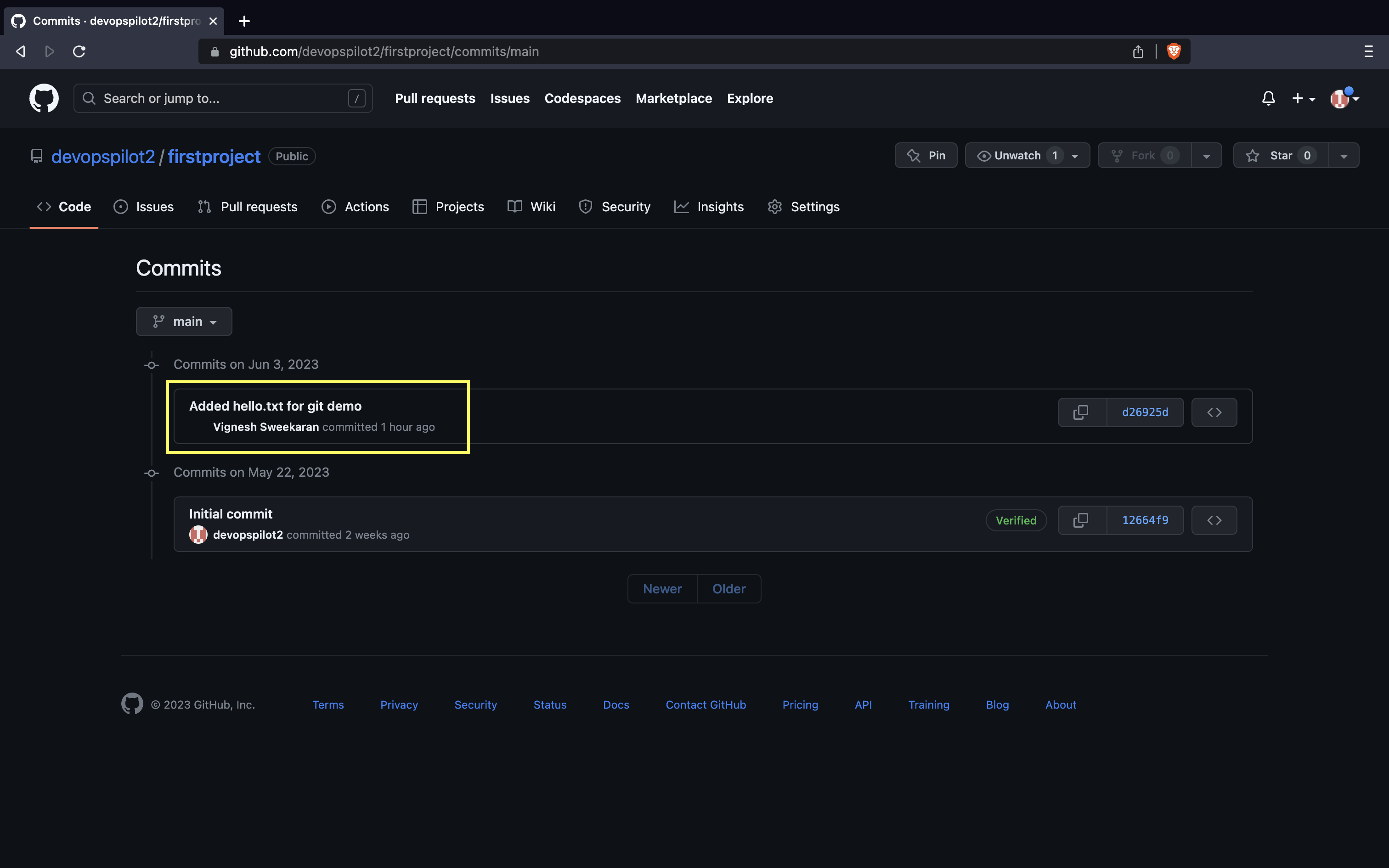
Here you can see all the commits pushed:
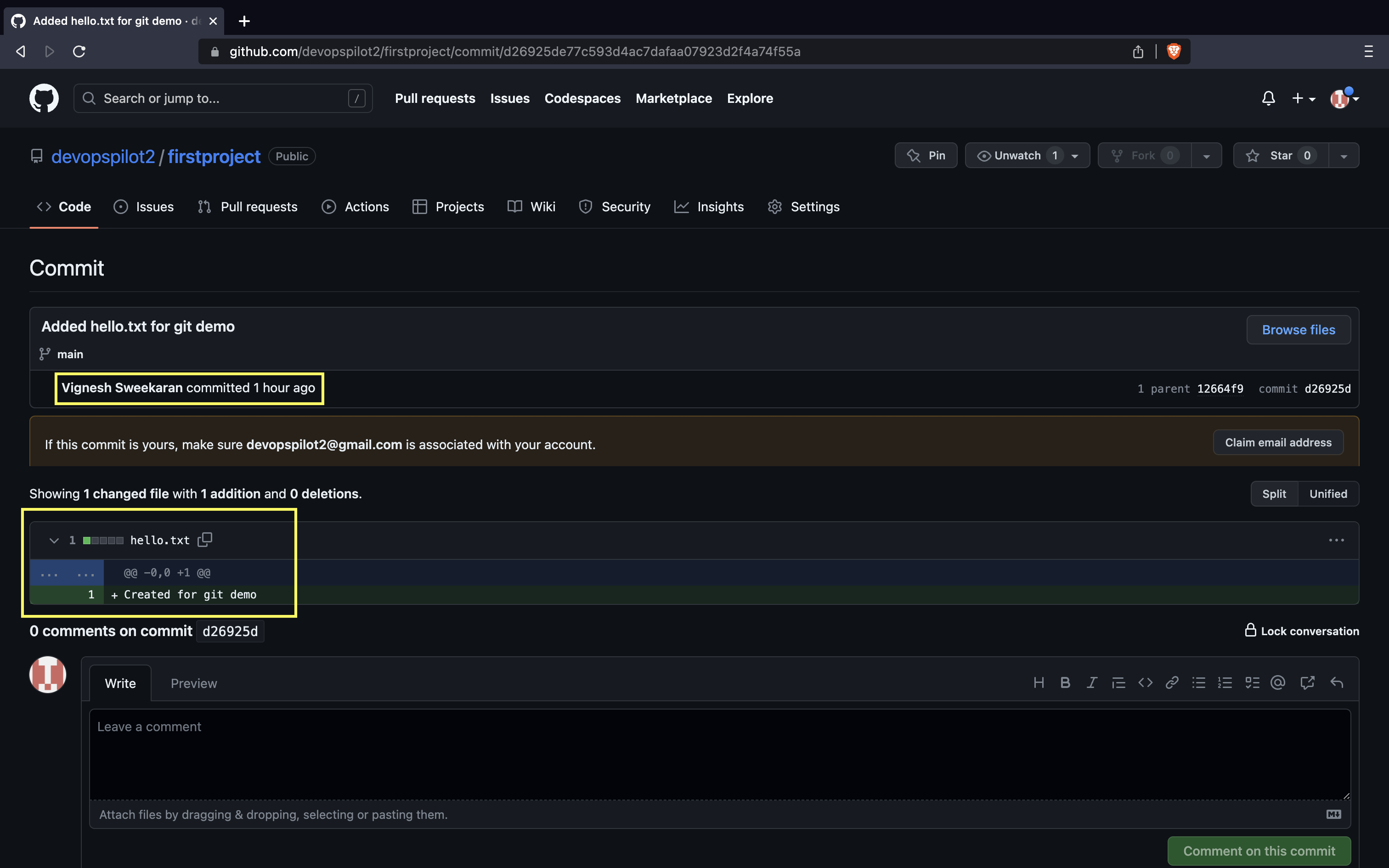
After clicking on one commit, you can see the changes made in the commit:
🧠 Quick Quiz — Pushing¶
What should you use as the password when pushing to GitHub via HTTPS?
📝 Want More Practice?¶
👉 Start Git Intermediate Quiz (20 Questions)
📬 DevopsPilot Weekly — Learn DevOps, Cloud & Gen AI the simple way.
👉 Subscribe here