Create Pipeline (Script)
Pipeline Script is often the first step toward understanding how Jenkins pipelines actually work under the hood.
In this tutorial, I explain:
- What a Pipeline Script job is in Jenkins
- How it differs from Freestyle jobs
- Where the Groovy-based pipeline script lives
- How stages and steps are defined
- How Jenkins executes the pipeline end to end
Pipeline Script helps you:
- Understand pipeline flow before moving to Jenkinsfile
- Experiment quickly without committing code
- Learn core pipeline concepts clearly
What is a Pipeline Script?¶
Pipeline Script in Jenkins allows you to define your build process using Groovy code directly in the Jenkins web interface.
Unlike Freestyle jobs, which rely on UI checkboxes and dropdowns, Pipeline Script gives you:
- Code-based configuration: Use logic, loops, and conditionals.
- Durability: Running pipelines survive Jenkins restarts.
- Visualized Stages: Clear feedback on which stage (Build, Test, Deploy) failed.
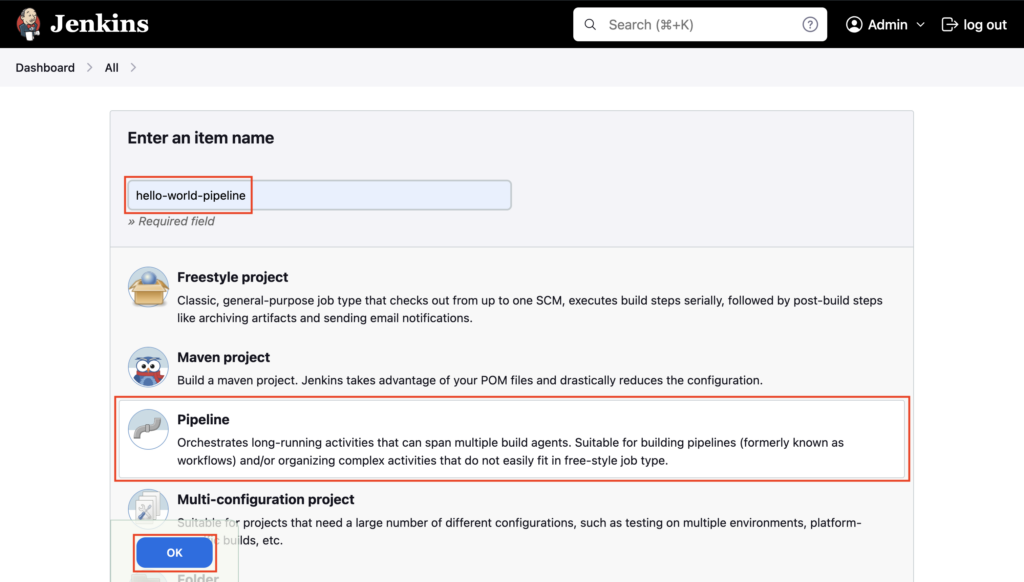
Goto Jenkins dashboard, click on New Item
Enter the Pipeline name hello-world-pipeline, select Pipeline, and then click OK
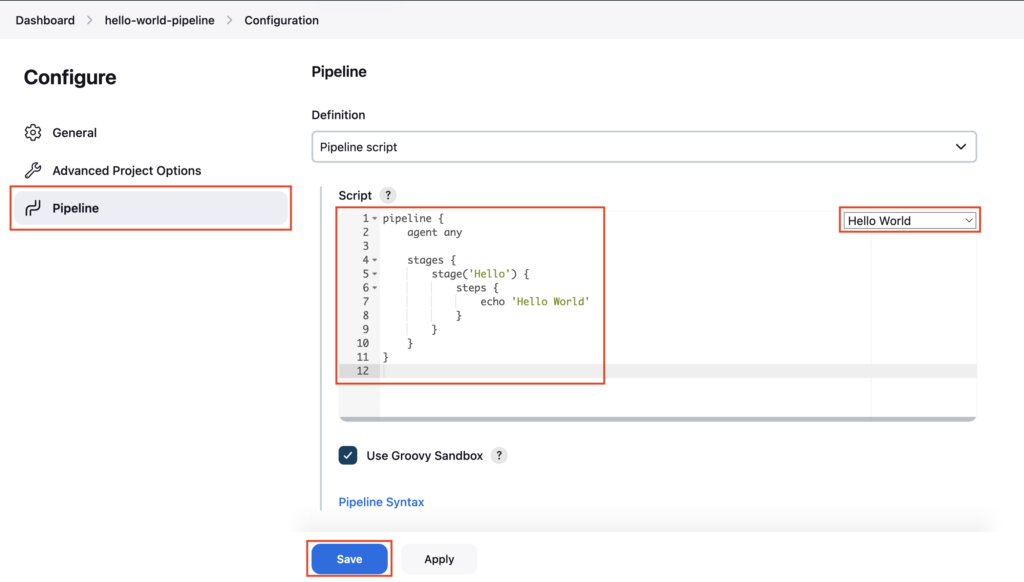
Select the Pipeline section, under Definition choose Pipeline script, and choose Hello World, sample pipeline script is added, and click on Save
In this, we have the Hello stage, which will execute an echo command to print Hello World to the Console Output.
Understanding the Script Structure¶
The script follows a specific hierarchy:
pipeline: The wrapper for the entire job.agent any: Tells Jenkins to run this on any available node (executor).stages: Blocks that define the sequence of tasks (e.g., Build, Test).steps: The actual commands (likesh,echo,git) inside a stage.
Note: In this method, the Groovy-based pipeline script lives directly in the Jenkins job configuration (specifically in the
config.xmlfile on the Jenkins controller), not in an external Git repository.
Reference: Jenkinsfile Syntax
Click on Build Now
Pipeline Execution Flow¶
When you trigger the build, Jenkins executes the pipeline end-to-end:
- Parses the Script: Jenkins reads the Groovy syntax.
- Allocates a Node: Based on
agent any, it finds an available executor. - Runs Stages: It executes
Hellostage. - Executes Steps: It runs the
echocommand. - Finalizes: Reports the build status (Success/Failure).
Goto Console Output, Hello World is printed on the logs using the echo command. In this way, you can execute any shell commands from the pipeline script.
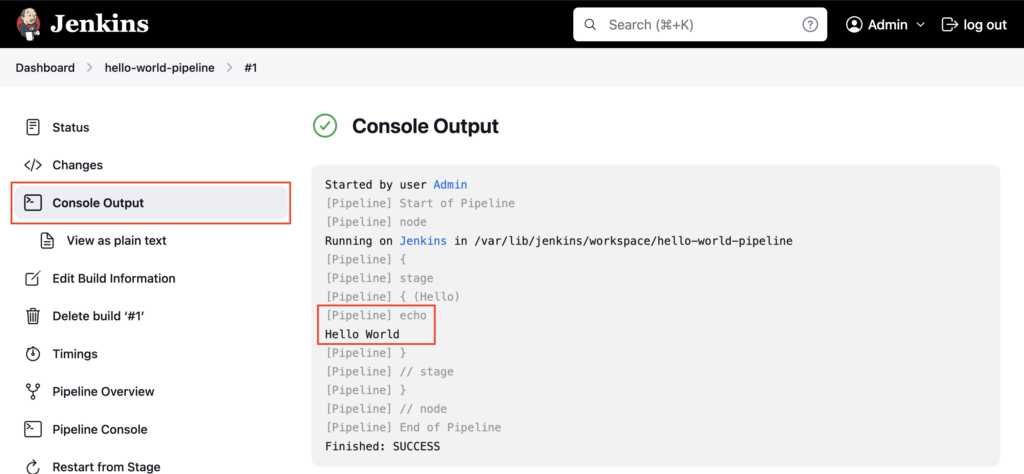
This way of writing the pipeline script in Jenkins UI is used mostly for testing purposes only. Since the script changes are not trackable.
The better way is to write the pipeline script in Jenkinsfile and store it in a GitHub repository.
Important Tips¶
Tip
Sandbox: Inline scripts run in a Groovy Sandbox to prevent malicious code execution. Some advanced Groovy methods might require administrator approval via "In-process Script Approval".
Note
Limitations: Inline scripts are hard to review and verify since they are part of the Jenkins configuration, not git. Use them only for quick prototypes or very simple administrative tasks.
🧠 Quick Quiz — Pipeline Script¶
Which language is used to write a Jenkins Pipeline Script?