How to configure free single Let’s Encrypt SSL/TLS Certificate with NGINX for multiple subdomains and autorenew certificate
Prerequisites
- Have NGINX or NGINX Plus installed.
- Own or control the registered domain name for the certificate.
- Create a DNS record that associates your domain name and your server’s public IP address.
Reference:
- How to install nginx
- How to purchase a free domain using freenom
- How to add a DNS record in freenom domain registrar
- How to configure Free Let’s Encrypt SSL/TLS Certificates with NGINX
What is certbot
Certbot is a agent for letsencrypt that runs in a server to complete the letsencrypt challenge, request a certificate and get a certificate.
What is Letsencrypt challenge
Letsencrypt want to verify that you own the domain. So using certbot it will host some files in /.well-known/acme-challenge/ folder and serve this files publicly using nginx webserver.
Once it verifies the files, the challenge is completed and it will issue the certificate for the requested domain.
How to install cerbot
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install certbot
sudo apt-get install python3-certbot-nginx
Create some sample application
To test multiple subdomains, we need some sample applications. Lets create 3 docker containers with sample python flask application.
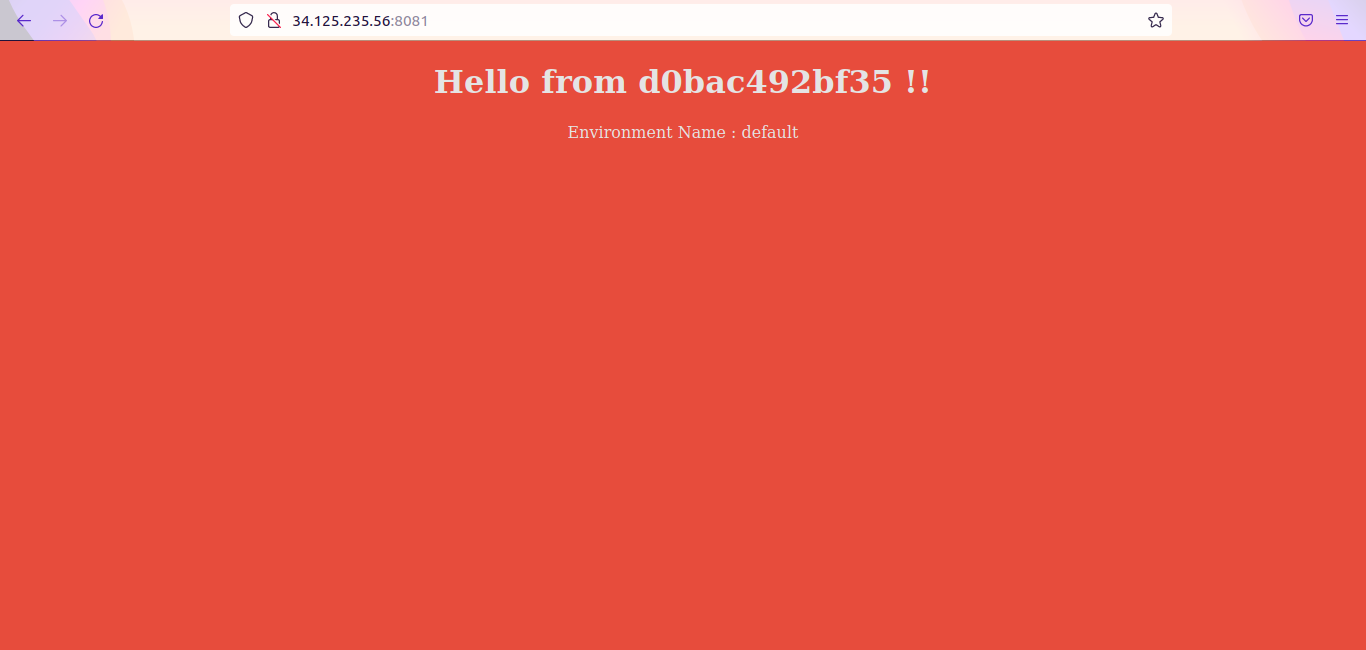
docker run -d -e APP_COLOR=red -p 8081:5000 vigneshsweekaran/helloworld-flask:latest
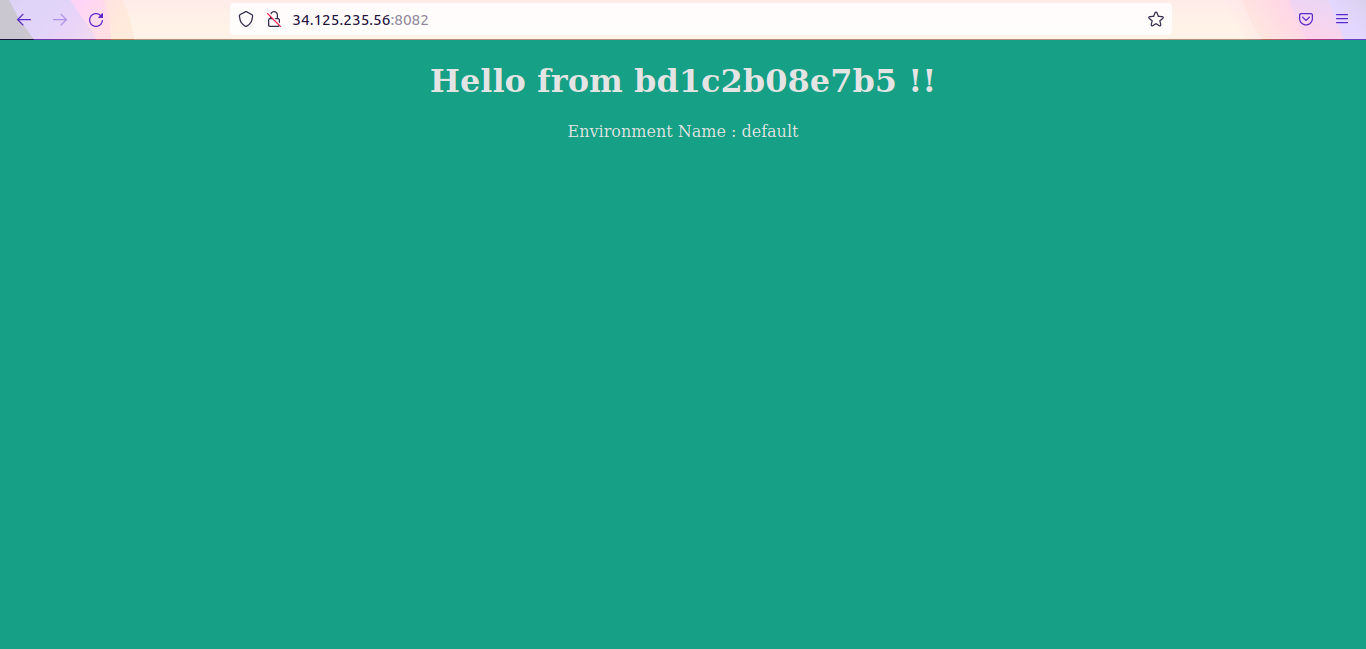
docker run -d -e APP_COLOR=green -p 8082:5000 vigneshsweekaran/helloworld-flask:latest
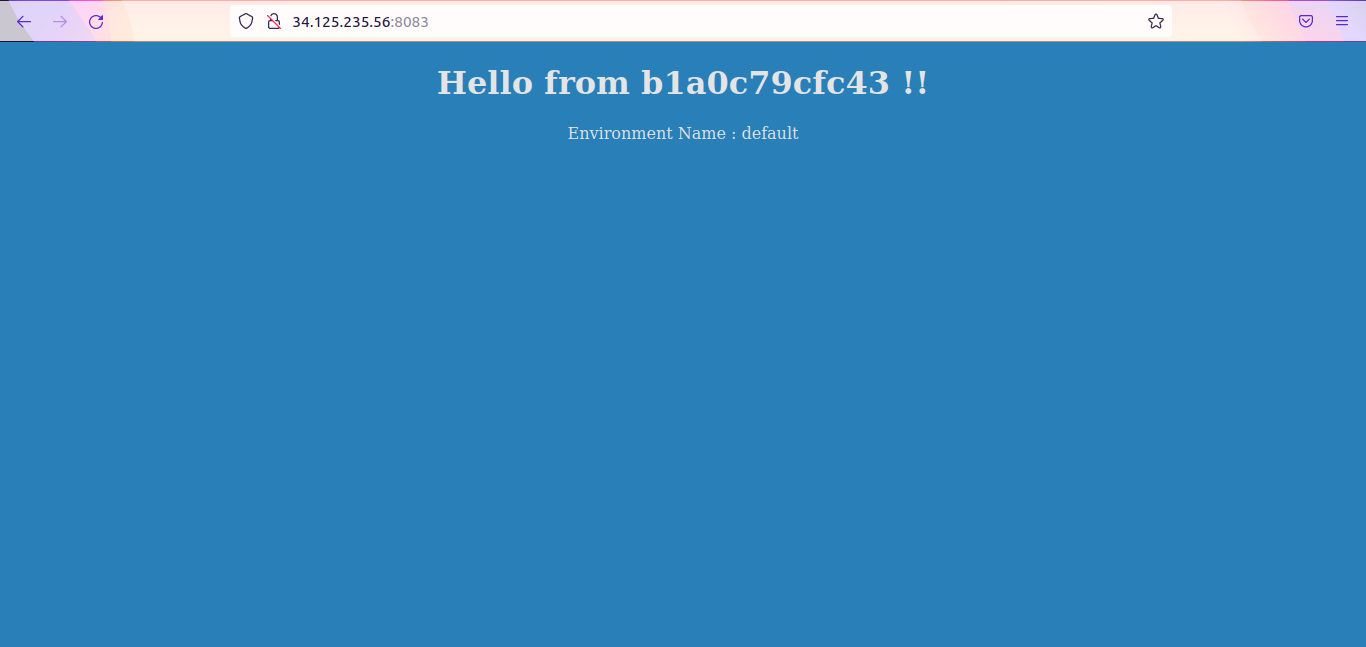
docker run -d -e APP_COLOR=blue -p 8083:5000 vigneshsweekaran/helloworld-flask:latest
Now we created 3 docker containers which runs on port 8081,8082 and 8083
Now open the browser and verify the applications are running.
IP-address:8081 –> Should show background color as red
IP-address:8082 –> Should show background color as green
IP-address:8083 –> Should show background color as blue
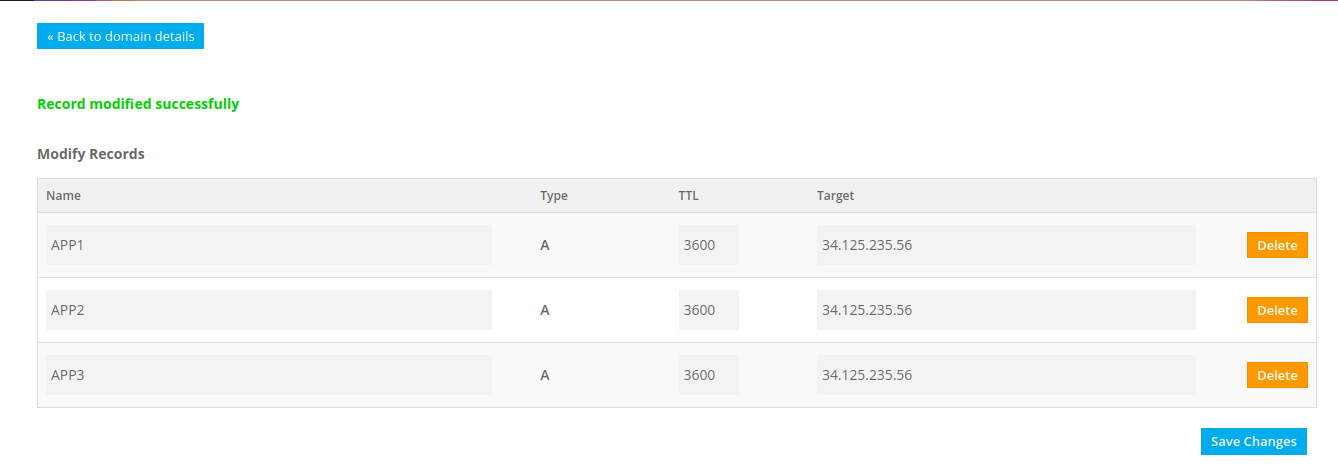
Configure DNS record in Domain registrar
app1.devopspilot.tk –> Public IP-address
app2.devopspilot.tk –> Public IP-address
app3.devopspilot.tk –> Public IP-address
Note :
- Public IP-address –> Public IP-address of your server, where 3 docker containers are running.
- Make sure ports 8081, 8082 and 8083 are open.
- Replace devopspilot.tk with your domain name.
Configure Nginx
Remove the default configuration file in nginx
sudo rm -f /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
Create new config file devopspilot.tk.conf in /etc/nginx/conf.d/ folder and put the following content
Info: Configuration file name can be anything
sudo vi /etc/nginx/conf.d/devopspilot.tk.conf
Replace devopspilot.tk with your domain name in config file
server {
listen 80;
server_name app1.devopspilot.tk;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8081;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name app2.devopspilot.tk;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8082;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name app3.devopspilot.tk;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8083;
}
}
Run the following command to check for syntax error in conf file
sudo nginx -t
Output :
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Run the following command to reload the nginx webserver
nginx -s reload
Now open the browser and verify whether applications are mapped to subdomains.
app1.devopspilot.tk –> Should show background color as red
app2.devopspilot.tk –> Should show background color as green
app3.devopspilot.tk –> Should show background color as blue
Change the devopspilot.tk to your domain name and run the below command.
It will complete the letsencrpt challenge, generate the certificate and map the certificate path in devopspilot.tk.conf conf file
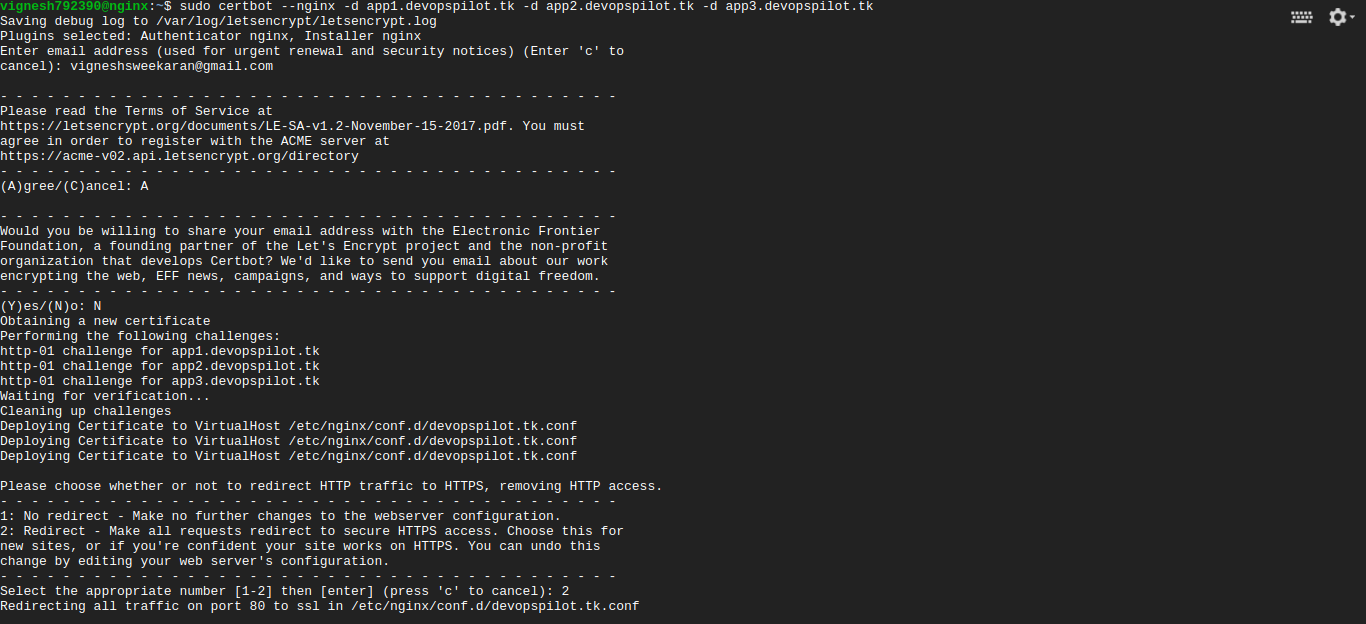
sudo certbot --nginx -d app1.devopspilot.tk -d app2.devopspilot.tk -d app3.devopspilot.tk
It will ask for email address, agree the terms and conditions, certificate will be issued and finally enter 2 to automatically redirect http to https
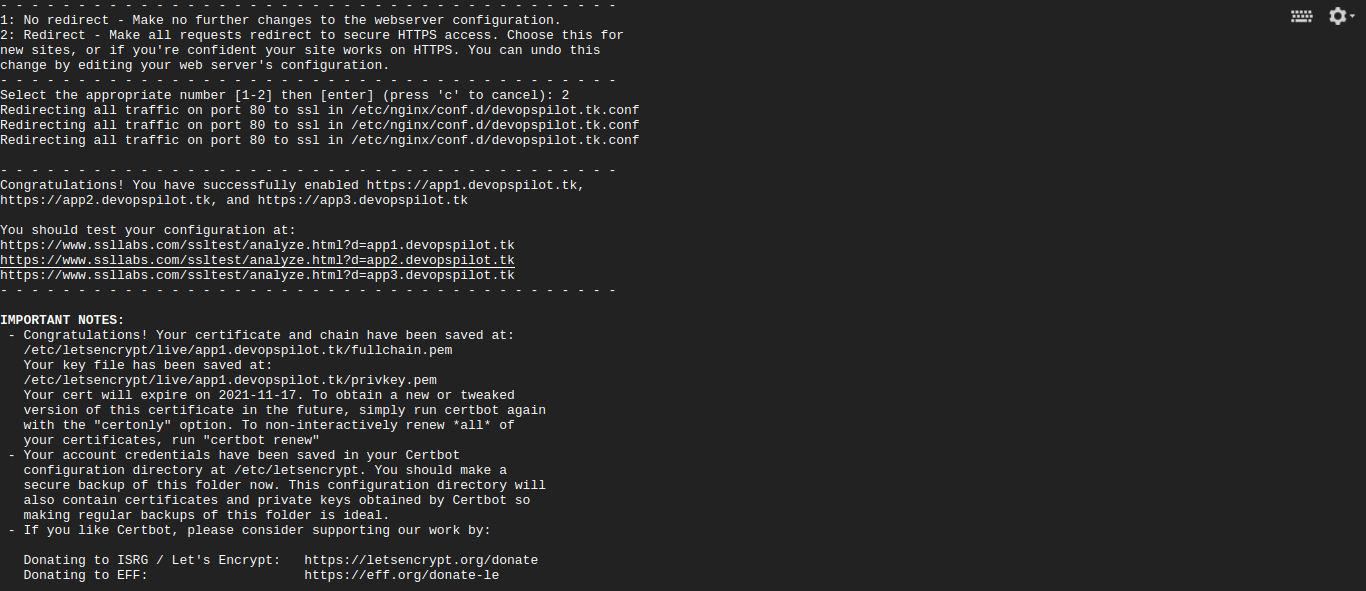
Check the nginx conf file /etc/nginx/conf.d/devopspilot.tk.conf which was updated by certbot
Now the nginx conf file looks like below.
server {
server_name app1.devopspilot.tk;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8081;
}
listen 443 ssl; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/app1.devopspilot.tk/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/app1.devopspilot.tk/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot
include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf; # managed by Certbot
ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem; # managed by Certbot
}
server {
server_name app2.devopspilot.tk;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8082;
}
listen 443 ssl; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/app1.devopspilot.tk/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/app1.devopspilot.tk/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot
include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf; # managed by Certbot
ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem; # managed by Certbot
}
server {
server_name app3.devopspilot.tk;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8083;
}
listen 443 ssl; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/app1.devopspilot.tk/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/app1.devopspilot.tk/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot
include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf; # managed by Certbot
ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem; # managed by Certbot
}
server {
if ($host = app1.devopspilot.tk) {
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
} # managed by Certbot
listen 80;
server_name app1.devopspilot.tk;
return 404; # managed by Certbot
}
server {
if ($host = app2.devopspilot.tk) {
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
} # managed by Certbot
listen 80;
server_name app2.devopspilot.tk;
return 404; # managed by Certbot
}
server {
if ($host = app3.devopspilot.tk) {
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
} # managed by Certbot
listen 80;
server_name app3.devopspilot.tk;
return 404; # managed by Certbot
}
Wait for couple of minutes.
Go to browser and type the domain name and verify whether its changed to https
Go to browser and type http://app1.devopspilot.tk
Now it will automatically redirect to https://app1.devopspilot.tk

Now lets see how to automatically renew the certificates.
Letsencrypt certificates will expire after 3 months.
Create a cron job with certbot renew command. This job will daily run at 12 AM and check whether certificates are going to expire or not.
If it is going to expire it will regenerate the certificate and map the new certificate path in nginx conf file
Run the following command to create a cron job.
crontab -e
After running the crontab -e command it will open a file, type the below command and save the file.
0 12 * * * /usr/bin/certbot renew --quiet
Hurray! we have successfully configured the SSL/TLS certificate in nginx webserver.